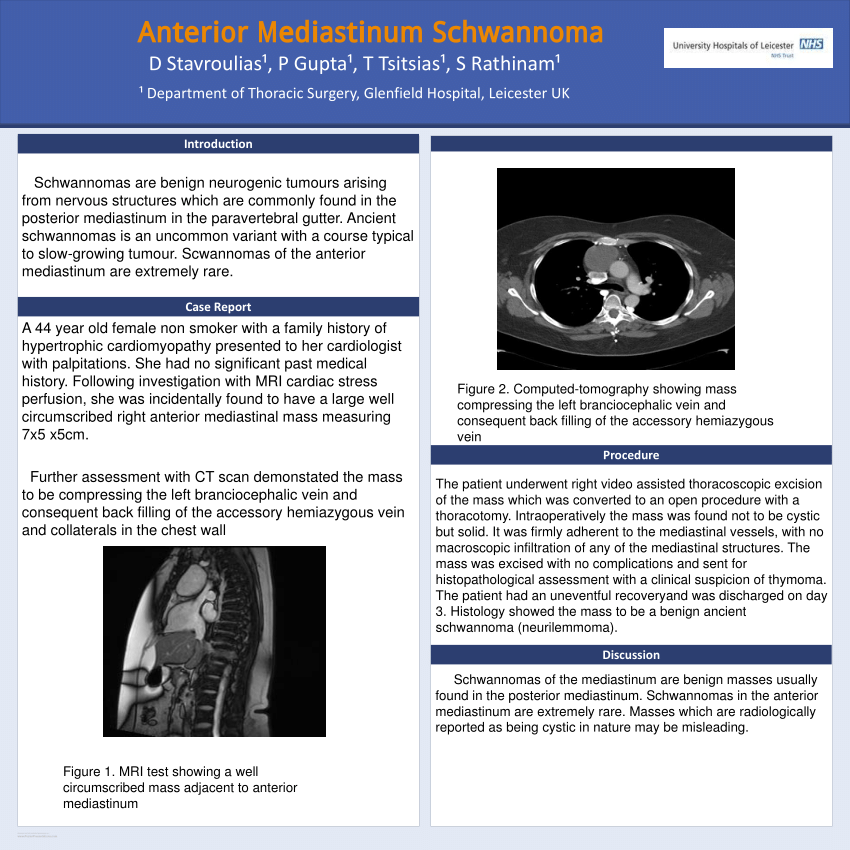
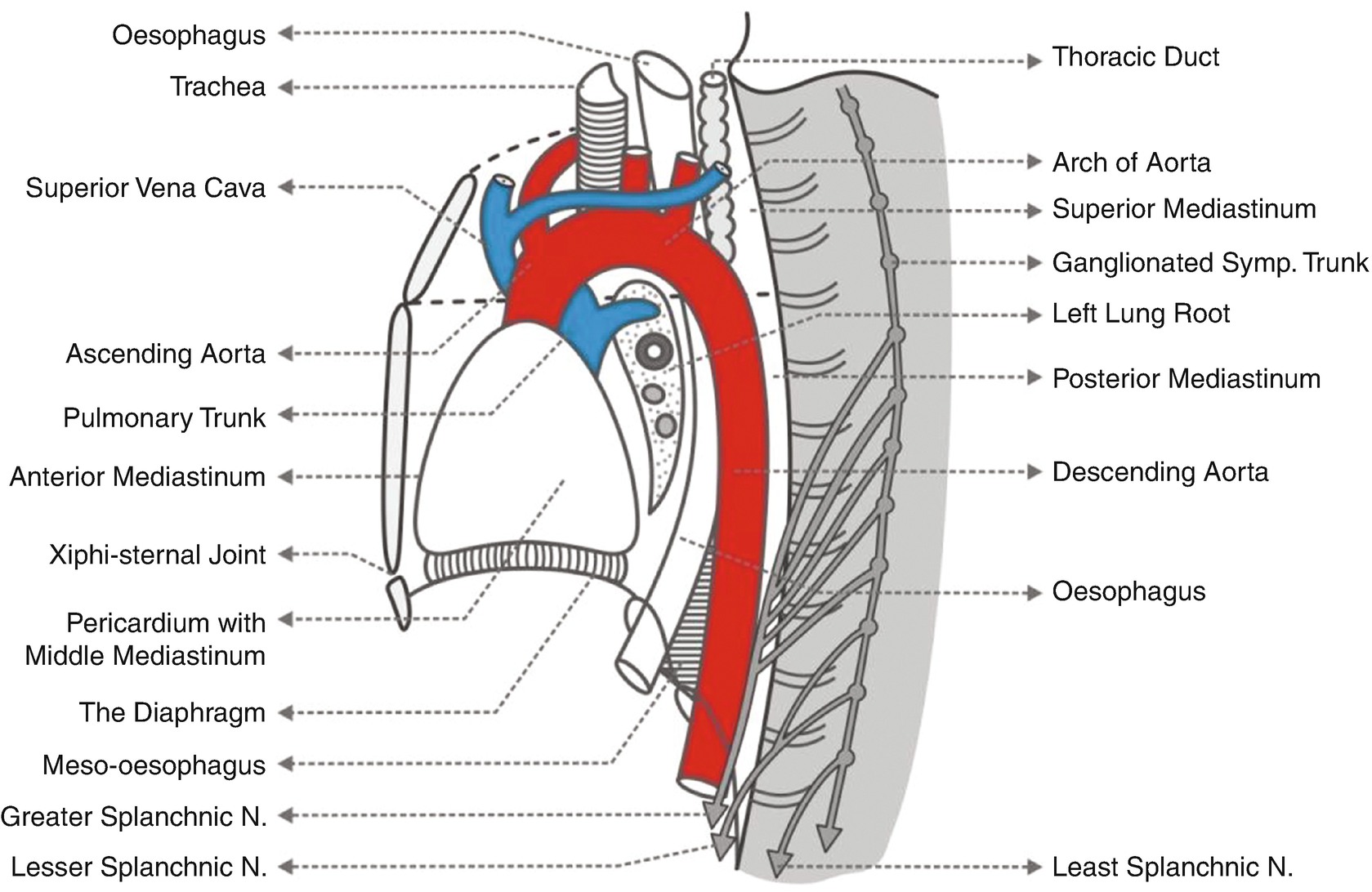
Paravertebral block is a technique where local anaesthetic is injected into the space adjacent to the vertebrae to block the spinal nerves as they emerge from the intervertebral foramen.
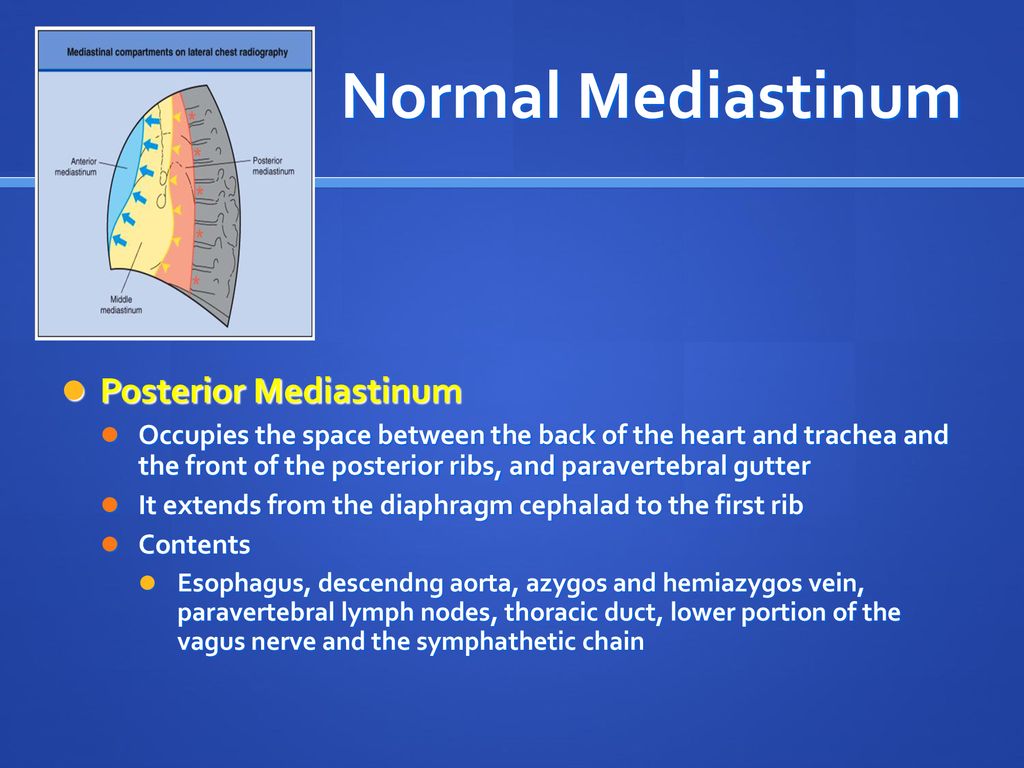
Contents of paravertebral gutter.
Iliopsoas is important for standing walking and running.
In trauma an increased thickness of the prevertebral space is a sign of injury and can be measured with medical imaging.
It may play a part in maintaining the position of the kidney which certainly becomes more mobile when the fat is depleted in severe weight loss.
An abundant fatty cushion that fills the paravertebral gutter above the iliac crest.
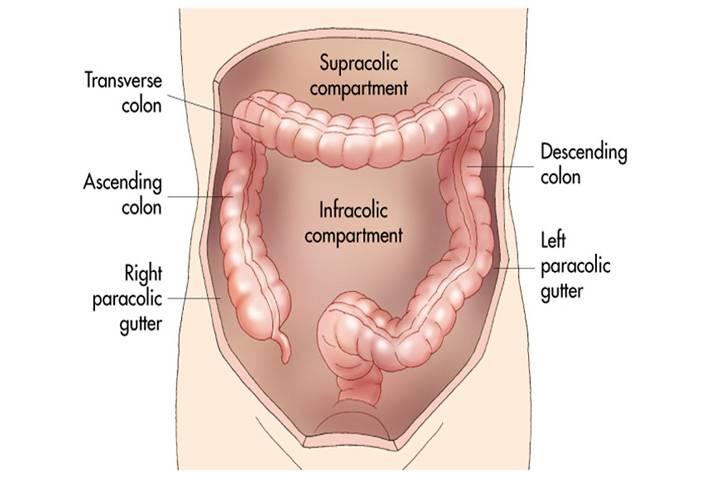
Fluid from an infected appendix can track up the right paracolic gutter to the hepatorenal recess.
It joins the iliacus muscle to form the iliopsoas muscle the strongest hip flexor of the human body.
The gutters are rounded outward on the patient s back.
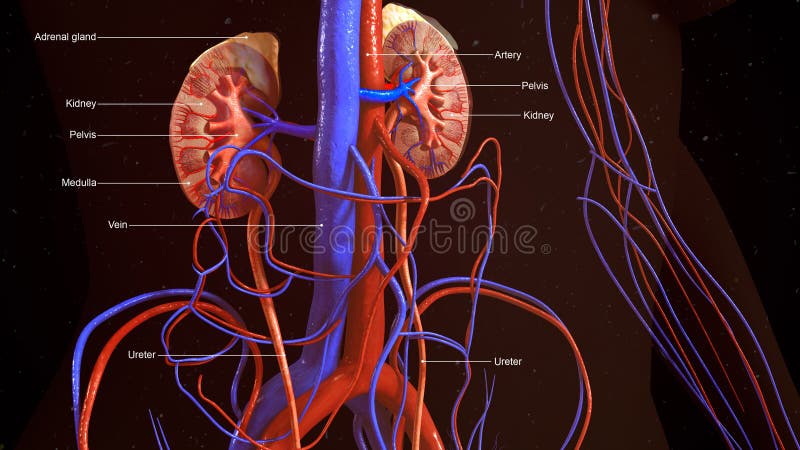
The perinephric fat.
Sulcus pulmonalis ta paravertebral gutter pulmonary sulcus farlex partner medical dictionary farlex 2012 want to thank tfd for its existence.
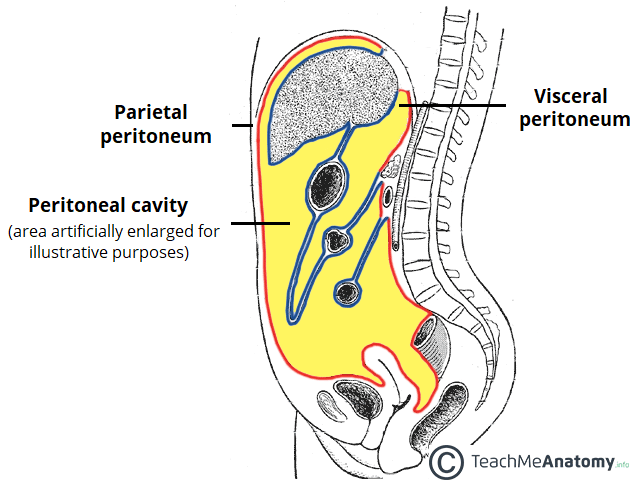
The kidneys lie retroperitoneally in the paravertebral gutter of the abdominal cavity.
Clinical significance bile pus or blood released from viscera anywhere along its length may run.
We would like to show you a description here but the site won t allow us.
Tge paravertebral gutters can be palpated or felt rather easily.
The deep vertical recess formed on either side of the thoracic cage by the posterior curvature of the ribs and containing the posterior portions of the lung.
Here the spinal nerves are devoid of covering fascia making them sensitive to the action of local anaesthetics.
These gutters are clinically important because they allow a passage for infectious fluids from different compartments of the abdomen.
The gutter part refers to the inside of the thoracic cage where the posterior lungs lie.
Often radiographers will place their thumbs on the patient s scapulae and place the patient into.
The patavertebral gutters are the rounded expanse of ribs formed when the back parts of the ribs curve from the outside edges towards the spinal column.
It includes the prevertebral muscles longus colli and longus capitis vertebral artery vertebral vein scalene muscles phrenic nerve and part of the brachial plexus.
A slight right anterior oblique rao when performing lateral chest x rays superimposes the posterior ribs as they are aligned to the divergent beam.
Psoas major is a triangular bilaterally paired muscle that forms part of the floor of the paravertebral gutter.